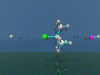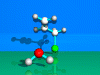SN1-Reaction
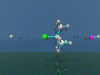
|
First Order Nucleophilic
Substitution.
The
nucleophilic substitution of a chlorine atom by a fluoride ion is described.
The reaction is catalysed by a proton.
A proton attacks the chlorine
atom and forms hydrochloric acid. A tertiary carbon cation is formed as an
intermediate (planar). From the right side hydrofluoric acid flies in. A
proton is lost and t-butylfluoride is formed.
|
SN2-Reaction

|
Second Order
Nucleophilic Substitution.
The
reaction of methylchloride with a fluoride ion is described.
The fluoride ion
(nucleophil) approaches from the right and substitutes the chloride ion in
the molecule. A transition state is passed, where all 3 hydrogen atoms and
the central carbon atom are arranged in a plane. Methylfluoride is
formed.
|
SN2t-Reaction
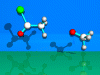
|
Second Order
Nucleophilic Substitution with a Tetragonal Transition State.
The reaction
of acetylchloride with a methoxy ion is described.
The methoxy ion
(nucleophil) adds to the carbonyl group of the acetylchloride (tetragonal
intermediate). The chloride ion will be lost, acetic acid methylester is
formed.
|
SN2'-Reaction
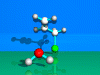
|
Second Order Vinylogous
Nucleophilic Substitution.
The hydrolysis
of allylchloride in water is described.
A water molecule
approaches the vinyl group of allylchloride at position 1 an substitutes the
chloride ion at position 3. Hydrochloric acid is formed. The reaction product
is allylic alcohol (propen-3-ol).
|
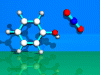
|
Electrophilic Aromatic
Substitution
The
nitration of phenol by a NO2 cation is described.
The cation (linear)
approaches at o-position of the phenole molecule and substitutes a hydrogen
atom. The intermediate has a tetragonal structure. o-nitrophenole is the
product.
|
|
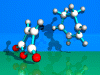
|
Diels-Alder-Reaction
Pericyclic
4+2 Cycloaddition.
The reaction of
cyclohexadiene with maleic acid anhydride is described. A bicyclic ring
system is formed. The reaction runs in concerted matter.
|
|

|
E1cb-Elimination
Formation
of styrene.
The elimination of HCl promoted
by a methoxide anion is described. Styrene is formed. First the
chloroethylbenzene is deprotonated then the chloride-ion is lost.
|
|
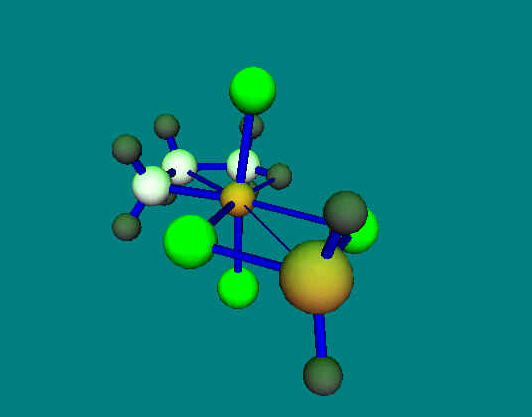
|
Ziegler-Type-Catalysis
Addition
of an alkylgroup (methyl) to ethylene at the active site of a Ziegler-type
catalysator [TiCl4 AlH2CH3].
|